Sága Wi-Fi 7 Routers
Designed for peak performance and easy refurbishment.
Find out more
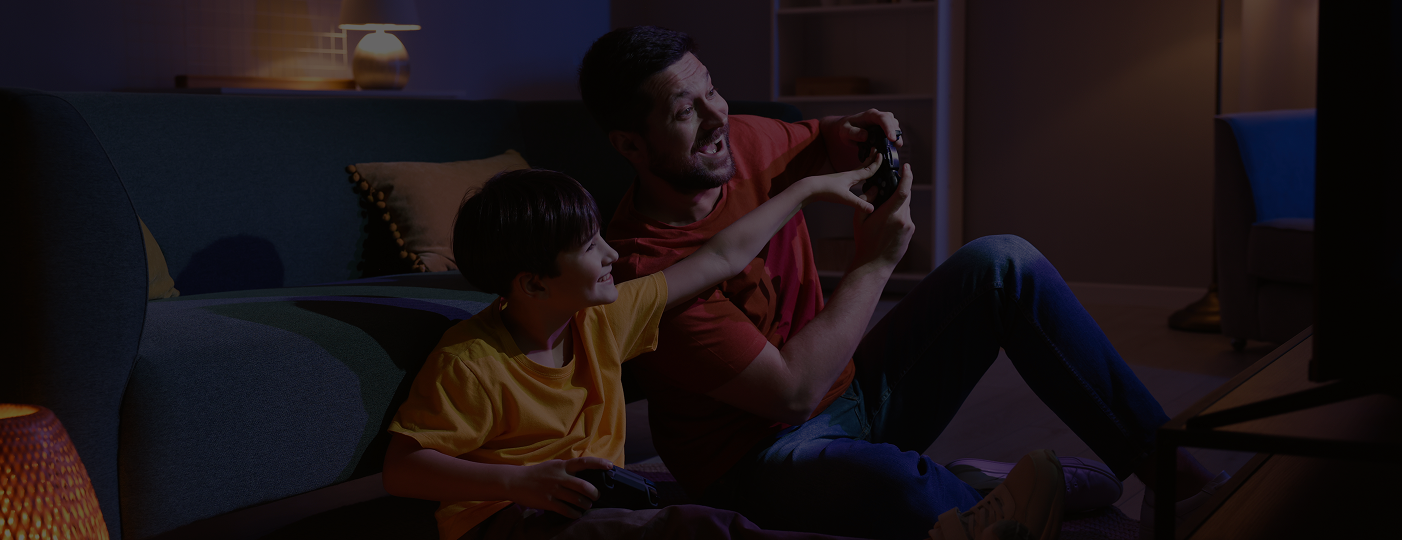




Wi-Fi Configurations let ISPs design networks that balance cost, performance, and customer demand. From dual- vs. tri-band setups to flexible antenna and port options, providers can tailor Wi-Fi deployments to their market needs, ensuring high-quality service without unnecessary complexity or expense.
Wi-Fi 7 certification does not always require all three bands, with many cases in which a dual-band setup is the most cost-efficient option. By omitting the 6 GHz band, operators can reduce hardware complexity and cost, making advanced Wi-Fi 7 performance more accessible to a broader customer base.
At the same time, tri-band designs are essential for households that need greater capacity, providing an additional high-speed band to ease congestion, support more devices, and unlock the full potential of Wi-Fi 7 in dense, high-usage environments.
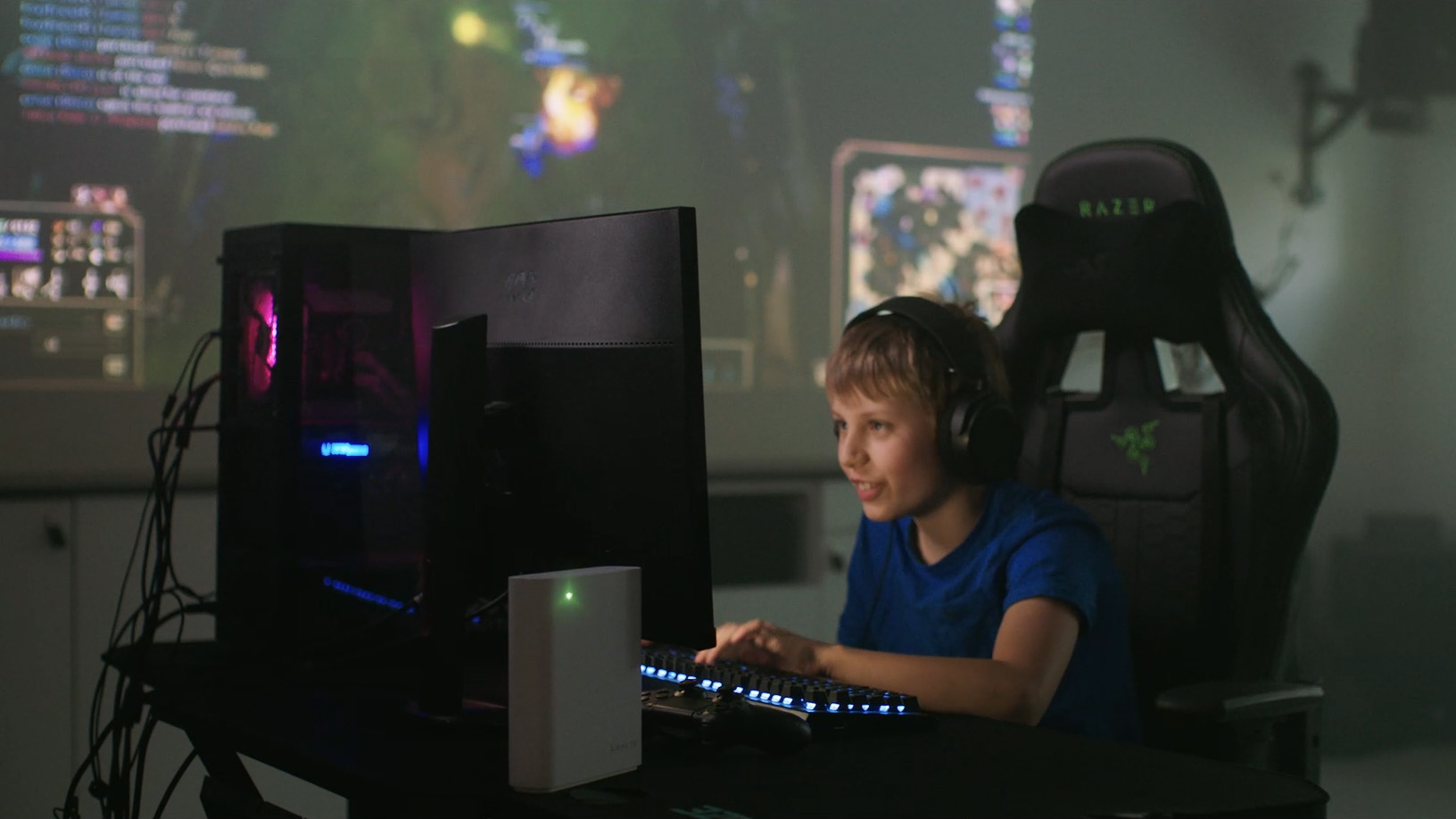


Antenna design has a direct impact on throughput and efficiency, so choosing between configurations like 2+4+2 and 2+4+4 antennas, allows ISPs to align performance with individual customer needs.
A 2+4+2 setup can reduce hardware cost while still delivering strong tri-band performance, whereas a 2+4+4 configuration provides additional spatial streams for higher throughput and improved performance in demanding environments.
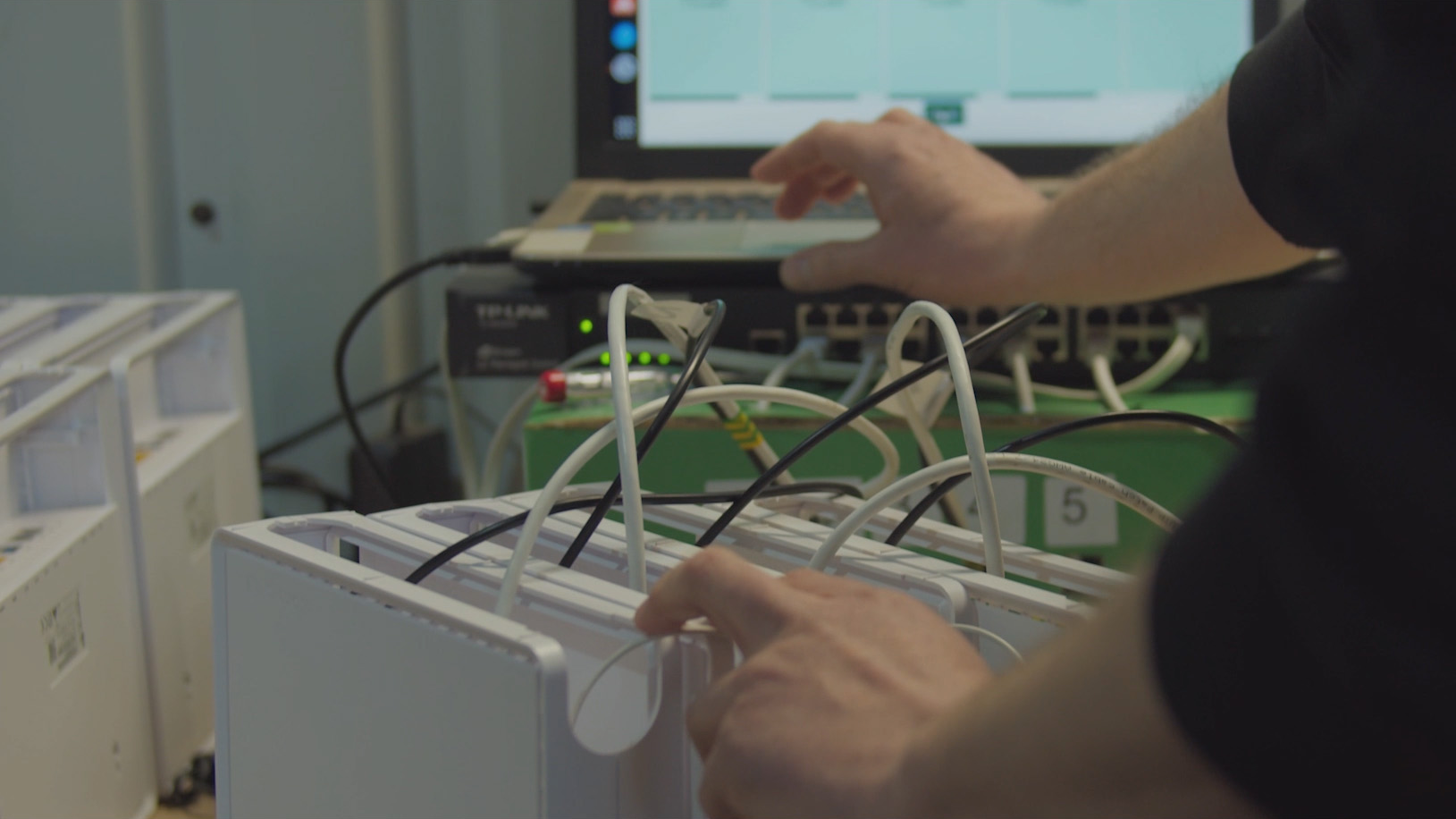

Supporting both 2.5G and 10G WAN/LAN port configurations gives ISPs the flexibility to meet a wide range of customer and deployment requirements. While some scenarios benefit from the ultra-high throughput of 10G ports, many residential environments do not require that level of performance.
Offering both options allows operators to tailor their hardware choices to actual demand, ensuring an optimal balance of cost, capability, and future-readiness.


Wi-Fi ROUTERS
Dual-band — 2.5G WAN — Optional VoIP

Wi-Fi ROUTERS
Tri-band — 2.5G WAN — Optional VoIP

Wi-Fi ROUTERS
Tri-band — 2.5G WAN — Optional VoIP

Wi-Fi ROUTERS
Tri-band — 10G WAN — Optional VoIP

Wi-Fi ROUTERS
Tri-band — 10G PON (1-Box) — Optional VoIP


| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |